
In an effort to raise awareness surrounding addiction and recovery, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) has made September National Recovery Month. Every September, SAMSHA assigns a theme to the campaign and promotes their mission in communities across the country in an attempt to bring more understanding and erase the stigma surrounding addiction.
National Recovery Month 2017
This year’s theme is “Join the Voices for Recovery: Strengthen Families and Communities”. The basis around this theme is uniting families and communities together to fight addiction and support recovery. SAMSHA has chosen to focus on uniting families and communities in the wake of the opioid epidemic that has been sweeping across the nation in previous years.

With the opioid epidemic beginning largely with prescription opioids, SAMSHA is urging parents to talk to their kids about the dangers of medications, including prescription opioids, and educate families on keeping their prescription medications locked up and out of reach to children. For more information on this year’s National Recovery Month theme, visit https://www.recoverymonth.gov/.
What’s New This Year?
While drug addiction is not a new ailment to our country, we have seen some recent changes in trends across the United States. With a growing number of individuals affected by the opioid epidemic, experts have noticed increasing trends in addiction among rural and non-city residents. This is a newer trend that makes it more difficult to detect and track the distribution and sale of the drug. Many rural areas have far fewer people per square mile than cities do, leaving miles of un-patrolled roads and communities open for trafficking.
Previously, anti-drug campaigns were centered around inner-city schools, community centers, churches, and other city-wide organizations. However with the increase in addiction rates in rural communities, National Recovery Month is urging communities to work together in fighting the opioid epidemic, among other addictions, as it potentially creeps into their communities and schools.
Education is one of the best methods for fighting opioid addiction. Beginning drug education with kids, even at a young age, can be key to helping them make the right decisions down the road. However, kids are not the only ones who can benefit from drug education. Many grown adults are unaware of the dangers that some unsuspecting drugs, such as prescription medications, can carry with them. When communities are educated on drug addiction, they are better equipped to handle situations like the opioid epidemic.
Be Socially Inclusive
SAMSHA is fighting hard to remove the stigma associated with drug addiction and abuse. For this year’s National Recovery Month, SAMSHA challenges communities to be socially inclusive in their efforts to educate residents on the dangers of drug use, as well as celebrate those who have made it to recovery.
SAMSHA takes the time to highlight individuals who may suffer from mental illness, urging communities to involve them in their fight against drug addiction. Providing support and education to individuals suffering from mental illness could help prevent them from reaching for drugs in the future, or encourage them to reach out if they already struggle with a drug addiction. Did you know: One study done by the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) found that over 50% of individuals suffering from a mental illness also struggle with a substance abuse problem?

Being socially inclusive also includes supporting individuals who are currently struggling with a substance abuse issue, and celebrating with those who are in recovery. Instead of shielding children from the facts and faces of drug abuse, it is important to include everyone in educational efforts throughout the community. Even allowing an individual who has previously struggled with drug addiction to be a part of the education process can be immensely beneficial, both for that individual and for the community they are educating.
Getting Everyone Involved
It is important to put a face to addiction, especially in communities that think “that never happens here”. Often times residents are shocked to learn that it does happen here, and it happens to people just like you and I. Removing the stigma associated with drug addiction can help bring people forward to tell their stories share in their recovery success.
Community organizations can help too. Schools are a great place for drug education to begin, but it doesn’t have to stay there. Fire departments, police departments, local churches, food banks, homeless shelters, and even book clubs and country clubs can join in on the mission. Addiction affects everyone, not just the shadowy figures depicted in movies. Supporting drug education in your area means you are supporting the entire community, not just a select group of people. Everyone has a chance to get involved and make a difference!
Get Help Today
Have you suffered from an addiction in your past? Do you have a loved one that is suffering from addiction? We are here to support you, your loved ones, and your community, and want to answer any questions you may have about addiction or treatment. Our goal is to get clients set up with the professional help and support they need to treat their addiction.
Our addiction treatment specialists are specifically trained to help you find treatment that fits your needs or the needs of your loved one and their addiction. Our addiction treatment specialists are available around the clock, and your call is always confidential. Give us a call today and let us help you.
For More Information On “National Recovery Month” Be Sure To Check Out These Additional Resources From DrugRehab.org:
- The Risk Factors For Substance Abuse – What You Need To Know
- How Do I Get My Loved One Into Rehab?
- Understanding A Heroin Use Disorder
- Is Addiction Genetic Or Environmental?
- Environmental Risk Factors for Developing an Addiction
Sources
American Psychiatric Association – Implementing Dual Diagnosis Services for Clients With Severe Mental Illness










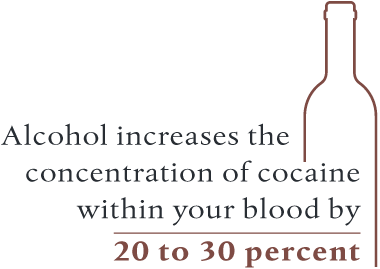 For individuals who aren’t accustomed to consuming alcohol with crack, the potential for a fatal overdose skyrockets. Alcohol can actually make it easier for your body to absorb cocaine, which increases the concentration of cocaine within your blood by 20 to 30 percent. From this effect, a person could overdose if they take an amount they are typically used to when using the drug alone.
For individuals who aren’t accustomed to consuming alcohol with crack, the potential for a fatal overdose skyrockets. Alcohol can actually make it easier for your body to absorb cocaine, which increases the concentration of cocaine within your blood by 20 to 30 percent. From this effect, a person could overdose if they take an amount they are typically used to when using the drug alone.
 Ativan is a brand name medication of the benzodiazepine (benzo) drug lorazepam. As a benzo, it’s a central nervous system (CNS) depressant, which means it slows several important bodily functions, including breathing rates, heart rate, and temperature. The
Ativan is a brand name medication of the benzodiazepine (benzo) drug lorazepam. As a benzo, it’s a central nervous system (CNS) depressant, which means it slows several important bodily functions, including breathing rates, heart rate, and temperature. The 
 Detox can be emotionally strenuous as well, which is another reason detoxing in a facility is so important. The facility’s staff will comfort you during this time, answering any questions you may have, or will simply provide an ear and any emotional support you may need.
Detox can be emotionally strenuous as well, which is another reason detoxing in a facility is so important. The facility’s staff will comfort you during this time, answering any questions you may have, or will simply provide an ear and any emotional support you may need.

 When used as a medical treatment, the prescribing doctor should gradually taper you off of the drug as to avoid unpleasant side effects of withdrawal. These professionals are trained and understand how to best do this to avoid any complications and further strain to your physical and mental states.
When used as a medical treatment, the prescribing doctor should gradually taper you off of the drug as to avoid unpleasant side effects of withdrawal. These professionals are trained and understand how to best do this to avoid any complications and further strain to your physical and mental states.




 Codeine has been mixed with different drugs to treat various medical conditions, most commonly acetaminophen. There are various strengths of this drug combination, indicated in the title of the drug as Tylenol 2, Tylenol 3, and Tylenol 4. Tylenol 4 is the most potent of these medications, containing 60mg of codeine and 325mg of acetaminophen.
Codeine has been mixed with different drugs to treat various medical conditions, most commonly acetaminophen. There are various strengths of this drug combination, indicated in the title of the drug as Tylenol 2, Tylenol 3, and Tylenol 4. Tylenol 4 is the most potent of these medications, containing 60mg of codeine and 325mg of acetaminophen. While reducing the amount and frequency of opioids if you have a substance abuse issue is important, quitting abruptly can be extremely dangerous. Because your brain has become accustomed to a certain level of opioids binding with your opioid receptors, your body considers this new chemical balance to be the norm. If you suddenly stop taking opioids, then this level will come down too rapidly, resulting in withdrawal symptoms.
While reducing the amount and frequency of opioids if you have a substance abuse issue is important, quitting abruptly can be extremely dangerous. Because your brain has become accustomed to a certain level of opioids binding with your opioid receptors, your body considers this new chemical balance to be the norm. If you suddenly stop taking opioids, then this level will come down too rapidly, resulting in withdrawal symptoms.
 Alcohol abuse
Alcohol abuse

 Suboxone is a fairly new drug to the addiction treatment market. Intended to treat all types of opioid addiction in adults, Suboxone is actually a combination of two different types of drugs; buprenorphine and naloxone. Often prescribed for pain control,
Suboxone is a fairly new drug to the addiction treatment market. Intended to treat all types of opioid addiction in adults, Suboxone is actually a combination of two different types of drugs; buprenorphine and naloxone. Often prescribed for pain control, 
 With this tolerance generally comes increased or more frequent consumption of the drug, which can lead to serious long-term effects down the road. These
With this tolerance generally comes increased or more frequent consumption of the drug, which can lead to serious long-term effects down the road. These 
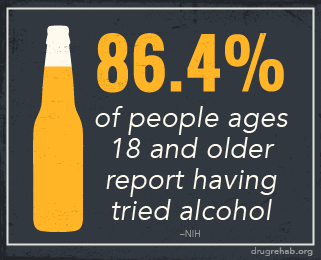 Alcohol withdrawals
Alcohol withdrawals
 In summary, alcohol withdrawal is not only a result of a physical demand of the chemical, but also the cognitive function in trying to maintain normal function.
In summary, alcohol withdrawal is not only a result of a physical demand of the chemical, but also the cognitive function in trying to maintain normal function.












 The
The 




